Morphological evaluation of the distal medial striate artery. A study with cadaveric material.
Abstract
SUMMARY:
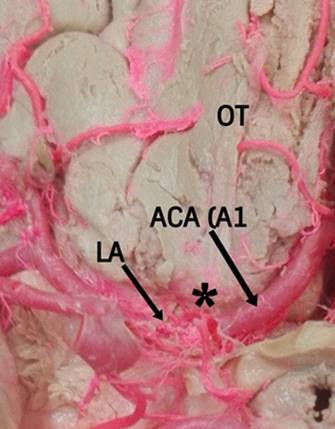
Background: The distal medial striated artery (DMSA) is a small, constant branch that emerges from the base of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and is directed backwards to irrigate internal structures such as the nucleous of the base.
Objective: This study proposes to evaluate the morphology of the DMSA, useful for clinical and surgical management that compromise this vascular structure.
Methods: The DMSA of 71 unclaimed male bodies, who underwent necropsy at the Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences of Bucaramanga-Colombia, were evaluated using the perfusion technique of vascular structures with polyester resin. Results: The DMSA was presented in four cases (2.8%) duplicated and with agenesis in 2.1% of the hemispheres. Its origin was 43.9% of the post-communicating segment of the ACA (A2), 10.8% of the pre-communicating segment of the ACA (A1) and 44.6% of the ACA junction site with the anterior communicating artery (AComA). The diameter of the DMSA was 0.5 ± 0.2 mm and its total length was 20.3 ± 4.1 mm. Sinuous trajectory was observed in 73 cases (51.4%). There was a superolateral relationship with the ACA in 48% of the samples. The DMSA was observed in 129 cases (90.9%) as a single trunk while in 6 cases (4.2%) it presented with a common trunk with the orbitofrontal artery (OF). The completion of the DMSA in the anterior perforated substance was given by a single trunk in 129 cases (90.9%) bifurcation in 9 cases (6.3%) and trifurcation in four cases (2.8%). The incidence of sinuous presentation and hypoplasia of the DMSA is considerably higher than previously reported.
Conclussions: The importance of the DMSA lies in its involvement with the surgical procedures and interventions of the anterior segment of the arterial cerebral circle, and in the complex clinical management that determine its injury in clinical practice.
Authors
Downloads
Keywords
- medial striate artery
- anterior cerebral artery
- recurrent Heubner artery
- anterior communicating artery
- collateral circulation
- autopsy
References
Andrés G, Saavedra G, Camejo C, Legnani C, Arciere B, Castro L. Neurol Arg. 2012;4(4):216-20.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuarg.2012.05.003
Boongird A, Duangtongphon P. Variation of the recurrent artery of Heubner in human cadavers. J Med Assoc Thail. 2009;92(5):643-7.
Dimitriu CP, Iliescu DM, Bordei P, Bulbuc I. Recurrent artery of Heubner - morphological variations. ARS Med. 2013;19(3):141-6.https://doi.org/10.2478/arsm-2013-0025
El Falougy H, Selmeciova P, Kubikova E, Haviarová Z. The variable origin of the recurrent artery of Heubner: An anatomical and morphometric study. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:10-2. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/873434
Feekes JA, Cassell MD. The vascular supply of the functional compartments of the human striatum. Brain. 2006;129(8):2189-201. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl158
Gasca-González OO, Delgado-Reyes L, Pérez-Cruz JC. Anatomía microquirúrgica del segmento extracerebral de la arteria recurrente de Heubner en población mexicana. Cir Cir. 2011;79(3):219-24.
Gomes FB, Dujovny M, Umansky F, Berman SK, Diaz FG, Ausman JI, et al. Microanatomy of the anterior cerebral artery. Surg Neurol. 1986;26(2):129-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(86)90365-4
Haroun RI, Rigamonti D, Tamargo RJ. Recurrent artery of Heubner: Otto Heubner's description of the artery and his influence on pediatrics in Germany. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(6):1084-8. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.6.1084
Izci Y, Seçkin H, Medow J, Turnquist C, Başkaya MK. Sulcal and gyral anatomy of the orbitofrontal cortex in relation to the recurrent artery of Heubner: An anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2009;31(6):439-45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0465-3
Kedia S, Daisy S, Mukherjee KK, Salunke P, Srinivasa R, Narain MS. Microsurgical anatomy of the anterior cerebral artery in Indian cadavers. Neurol India. 2013;61(2):117-21. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.111113
Loukas M, Louis RG, Childs RS. Anatomical examination of the recurrent artery of Heubner. Clin Anat. 2006;19(1):25-31. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20229
Maga P, Tomaszewski KA, Pasternak A, Zawilinski J, Tomaszewska R, Gregorczyk-Maga I, et al. Extra- and intracerebral course of the recurrent artery of Heubner. Folia Morphol. 2013;72(2):94-9. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.2013.0016
Miller SP, O'Gorman AM, Shevell MI. Recurrent artery of Heubner infarction in infancy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007;42(5):344-6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2000.tb00101.x
Sanabria-Pinilla KD, Quijano-Blanco Y, Huayta-Alarcón VA. Prevalencia de la Arteria Estriada Medial Distal en una Muestra de Poblaciones Colombiana y Peruana. Int J Morphol. 2019;37(3):997-1002. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022019000300997
Toyoda K. Anterior Cerebral Artery and Heubner's Artery Territory Infarction. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2012; 30:120-2. https://doi.org/10.1159/000333607
Zunon-Kipré Y, Peltier J, Haïdara A, Havet E, Kakou M, Gars D Le. Microsurgical anatomy of distal medial striate artery (recurrent artery of Heubner). Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34(1):15-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-011-0888-5
Copyright (c) 2020 Natalia García, Pedro Luis Forero Porras, Luis Ernesto Ballesteros Acuña (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The copy rights of the articles published in Colombia Médica belong to the Universidad del Valle. The contents of the articles that appear in the Journal are exclusively the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the Editorial Committee of the Journal. It is allowed to reproduce the material published in Colombia Médica without prior authorization for non-commercial use


 https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1844-2793
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1844-2793




















