LRBA in the endomembrane system
Keywords:
LRBA deficiency, primary immunodeficiences, apoptosis, autophagy, vesicle trafficking, Adaptor Proteins, signal transducingMain Article Content
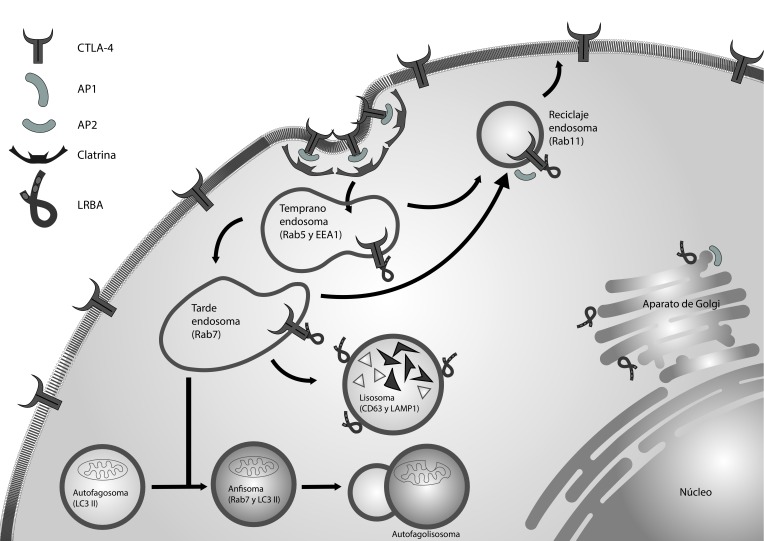
Bi-allelic mutations in LRBA (from Lipopolysaccharide-responsive and beige-like anchor protein) result in a primary immunodeficiency with clinical features ranging from hypogammaglobulinemia and lymphoproliferative syndrome to inflammatory bowel disease and heterogeneous autoimmune manifestations. LRBA deficiency has been shown to affect vesicular trafficking, autophagy and apoptosis, which may lead to alterations of several molecules and processes that play key roles for immunity.
In this review, we will discuss the relationship of LRBA with the endovesicular system in the context of receptor trafficking, autophagy and apoptosis. Since these mechanisms of homeostasis are inherent to all living cells and not only limited to the immune system and also, because they are involved in physiological as well as pathological processes such as embryogenesis or tumoral transformation, we envisage advancing in the identification of potential pharmacological agents to manipulate these processes.
Downloads

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The copy rights of the articles published in Colombia Médica belong to the Universidad del Valle. The contents of the articles that appear in the Journal are exclusively the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the Editorial Committee of the Journal. It is allowed to reproduce the material published in Colombia Médica without prior authorization for non-commercial use