Reply to a letter from Robert Colebunders entitled COVID-19: The African Enigma
Keywords:
SARS-CoV-2, Ivermectin, Respiratory Distress Syndrome, COVID-19, Causality, AfricaMain Article Content
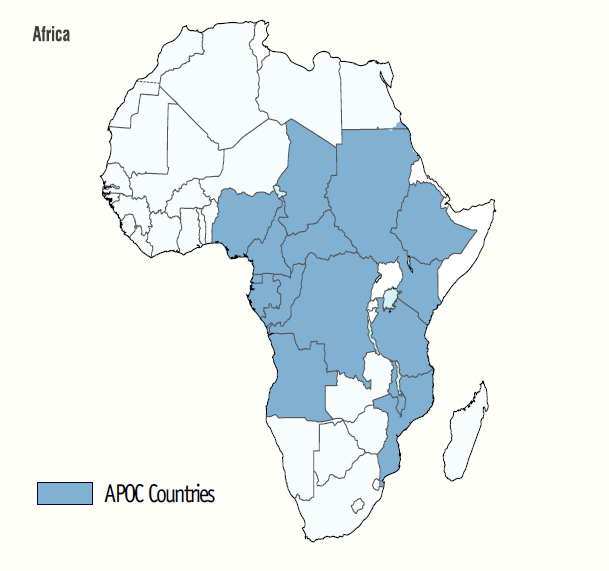
We thank Dr. Colebunders for his comments regarding our manuscript. Our study was an ecological study prompted by the low frequency of cases and deaths from the SARS-CoV-2 COVID-19 virus in some African countries. We agree with Dr. Colebunders that other factors could explain the observed association between APOC countries and COVID-19 mortality. However, these unmeasured confounders would have to be strongly associated with Covid-19 mortality to explain the observed 28% reduction. In updated information, as of 12-17-20, APOC countries had a 42% lower risk of death than the non-APOC countries, adjusted for confounders. (Not published)
Hellwig et al., in addition to reporting similar findings to ours for African and Asian countries, surmised that they may be connected to ivermectin’s ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication suggesting other pathways must exist to explain the persistence of such an inhibitory effect after serum levels of ivermectin have declined. As mentioned by Mbow et al. “, it is increasingly recognized that the immune system is shaped not only by genetics but also by environmental factors, such as exposure to microorganisms and parasites. This educates the immune system to protect against invading pathogens not only specifically but also nonspecifically through, for example, “trained immunity,” which involves the reprogramming of innate cells that, on secondary encounter with a pathogen, can show a stronger response.” Those infections, such as onchocerciasis, may downregulate immune responses and potentially inactivate the inflammatory signalling pathways that may induce acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), one of the causes of death in COVID-19 infected persons, seems very attractive explanation.
Downloads

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The copy rights of the articles published in Colombia Médica belong to the Universidad del Valle. The contents of the articles that appear in the Journal are exclusively the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the Editorial Committee of the Journal. It is allowed to reproduce the material published in Colombia Médica without prior authorization for non-commercial use

 https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4683-7987
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4683-7987