CyberKnife Radiosurgery for refractory bilateral trigeminal neuralgia. Case report
Keywords:
Radiosurgery, Rhizotomy, Microvascular Decompression Surgery, Microsurgery, Robotic Surgical Procedures, Intractable pain, Trigeminal neuralgiaMain Article Content
Case description:
A case of a 37-year-old female patient suffering from refractory bilateral trigeminal neuralgia is presented, she underwent various interventions such as acupuncture, block therapies and even microvascular decompression without effective pain relief.
Clinical findings:
Paresthesias and shooting-like twinges of pain intensity 10/10 in bilateral maxillary and mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerve, with nasal and intraoral triggers that made eating impossible, becoming increasingly severe since refractoriness to microvascular decompression and carbamazepine, triggering the twinges even during sleep, generating somnolence, depressive mood and social isolation.
Treatment and results:
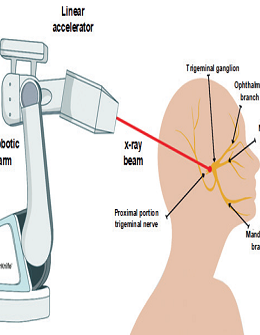
The patient was evaluated by an interdisciplinary neuro-oncology team, where, in accordance with the analysis of the brain magnetic resonance imaging and the patient's history, it was indicated to perform Cyberknife® radiosurgery in mono-fraction on the left trigeminal and subsequently treat the contralateral trigeminal. When treated with Cyberknife® radiosurgery, the patient reported absolute improvement in her pain for 2 years.
Clinical relevance:
Radiosurgery by CyberKnife is not yet the first line of management in trigeminal neuralgia, however, it should be considered since several studies have managed to demonstrate an increase in the quality of life of patients and pain relief in refractory or severe cases. of said pathology.
Merskey H, Bogduk N. Classification of chronic pain. Descriptors of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. 2.a ed. Seattle: IASP Press; 1994.
Alcántara MA, Sánchez CCI. Actualización en el manejo de la neuralgia del trigémino. Semer Med Fam. 2016; 42(4): 244-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semerg.2015.09.007 PMid:26643391
Li Y, Yang L, Ni J, Dou Z. Microvascular decompression and radiofrequency for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a meta-analysis. J Pain Res. 2019; 12: 1937-45. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S203141 PMid:31303785 PMCid:PMC6605044
Sanchez SL, Párraga RG. Descompresión microvascular para el tratamiento de la neuralgia del trigémino. Gac Med Bol. 2020;43(1): 67-73. https://doi.org/10.47993/gmb.v43i1.21
Green TH, Girgis F. Trigeminal neuralgia: medical management and surgical options. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2019; 33(1-2): 32-3. https://doi.org/10.1080/15360288.2019.1624676 PMid:31369323
Tian C, Wang X, Wu S, Liu Y, Luo R. Letter: pain outcomes following microvascular decompression for drug-resistant trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 2020;86(3): E353-4. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz461 PMid:31748783
Campero A, Ajler P, Campero Aa. Descompresión microvascular en neuralgia del trigémino: Reporte de 36 casos y revisión de la literatura. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5(12):441. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.142794 PMid:25379343 PMCid:PMC4220413
Liao J-J, Cheng W-C, Chang C-N, Yang J-T, Wei K-C, Hsu Y-H, et al. Reoperation for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression. Surg Neurol. 1997;47(6):562-8. DOI: 10.1016/S0090-3019(96)00250-9 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-3019(96)00250-9 PMid:9167781
Mora DI, Martínez SJE, Fernández HLS, Rosa GA, Jiménez PRE, Hidalgo CT. Análisis de decisión: coste-efectividad en el tratamiento quirúrgico de la neuralgia del trigémino. Rev la Soc Española Dolor. 2013;20(4):161-9. https://doi.org/10.4321/S1134-80462013000400003
Chumpitaz CV, Sayán SC, Ruíz RE, Franco QC, Eche HJ, Caldas CV, et al. Actualización de criterios diagnósticos y tratamiento de la neuralgia del trigémino. Odontol Sanmarquina. 2014; 16(1):44. https://doi.org/10.15381/os.v16i1.5379
Tavakol S, Jackanich A, Strickland BA, Marietta M, Ravina K, Yu C, et al. Effectiveness of gamma knife radiosurgery in the treatment of refractory trigeminal neuralgia: a case series. Oper Neurosurg. 2020;18(6):571-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz311 PMid:31620790
Romanelli P, Conti A, Redaelli I, Martinotti AS, Bergantin A, Bianchi LC, et al. Cyberknife Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia. Cureus. 2019;11(10): e6014. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.6014
Berti A, Ibars G, Wu X, Sabo A, Granville M, Suarez G, et al. Evaluation of CyberKnife radiosurgery for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. Cureus. 2018;10(5): e2598. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2598
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.2598
Lakshman V, Aal M, Karumanchi P, Jaleel A, Iyer A. Trigeminal neuralgia secondary to vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia treated with cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery. Asian J Neurosurg. 2019;14(3):978. DOI: 10.4103/ajns.ajns_53_18
https://doi.org/10.4103/ajns.AJNS_53_18
PMid:31497145 PMCid:PMC6703046
Calcerrada N, Sabés R. Efectividad, seguridad y estimación de costes del sistema de radiocirugía Cyberknife. 1st ed. Madrid: Agencia Laín Entralgo; 2005.
Ho CC, Khan SA, Whealy MA. Neuralgia trigeminal. UpToDate; 2020. Disponibel en: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/trigeminal-neuralgia
Fleetwood IG, Innes AM, Hansen SR, Steinberg GK. Familial trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2001;95(3):513-7. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.95.3.0513 PMid:11565877
International Headache Society. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 2018; 38(1):1-211. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102417738202
Serrano RAA, Martínez MJdeJ, Revuelta GR, Gómez AJL, Martínez AJJ, Ponce GJA, et al. Radiocirugía estereotáctica con acelerador lineal para el tratamiento de la neuralgia trigeminal. Experiencia de nueve años en una sola institución. Rev Neurol. 2014;59(06):249. https://doi.org/10.33588/rn.5906.2014177 PMid:25190337
Chaves JPG, de Oliveira TVHF, Francisco AN, Trintinalha MdeO, Carvalho NVP. Trigeminal neuralgia recurrence: a comparison of microvascular decompression and percutaneous balloon compression: a five years follow-up study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2021;79(1):51-5. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x-anp-2020-0115 PMid:33656112
Downloads

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The copy rights of the articles published in Colombia Médica belong to the Universidad del Valle. The contents of the articles that appear in the Journal are exclusively the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the Editorial Committee of the Journal. It is allowed to reproduce the material published in Colombia Médica without prior authorization for non-commercial use

 https://orcid.org/0009-0006-9582-189X
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-9582-189X